In this blog, we’ll delve into the dynamic ListView in Flutter, exploring its versatility and power, accompanied by a real-world code example.
Additionally, we’ll discuss how ListView differs from using a Column within a SingleChildScrollView and why ListView is often the preferred choice.
You can follow the official documentation to set up Flutter: Flutter Installation Guide.
Table of Contents

Brief of Dynamic listview in Flutter
A dynamic ListView in Flutter allows developers to create a scrollable list of widgets whose content can change dynamically.
This is particularly useful when dealing with data that can be updated or modified during runtime, such as fetching data from an API, handling user-generated content, or managing real-time data changes.
The Limitation of Column with SingleChildScrollView
While using a Column within a SingleChildScrollView is a valid approach to achieve a scrollable layout, it may not be the most efficient solution when dealing with large datasets or dynamic content.
ListView, on the other hand, is specifically designed for efficiently rendering only the visible items on the screen, leading to better performance and a smoother user experience.
Let’s delve into a real-world example to illustrate the implementation of a dynamic ListView in Flutter and compare it with a Column and SingleChildScrollView.
Example code of dynamic ListView
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: DynamicListViewExample(),
);
}
}
class DynamicListViewExample extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_DynamicListViewExampleState createState() => _DynamicListViewExampleState();
}
class _DynamicListViewExampleState extends State<DynamicListViewExample> {
List<String> data = ['Item 1', 'Item 2', 'Item 3', 'Item 4', 'Item 5'];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Dynamic ListView Example'),
),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: data.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return ListTile(
title: Text(data[index]),
// Add any additional widgets or functionality here
);
},
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
// Add a new item to the list
setState(() {
data.add('New Item');
});
},
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
Explanation of the Code:
- We have the same Flutter project structure as before, with a
DynamicListViewExampleStatefulWidget. - The
buildmethod of the state class returns a Scaffold widget containing an AppBar, a dynamic ListView, and a FloatingActionButton, similar to the previous example. - The key difference lies in the use of
ListView.buildercreating a dynamic ListView instead of a Column within a SingleChildScrollView. - The dynamic ListView efficiently manages the rendering of visible items on the screen, providing better performance for scenarios involving large datasets.
Example code of dynamic List with column
If you want to replace the ListView with a Column within a SingleChildScrollView, here’s the modified code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: DynamicColumnExample(),
);
}
}
class DynamicColumnExample extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_DynamicColumnExampleState createState() => _DynamicColumnExampleState();
}
class _DynamicColumnExampleState extends State<DynamicColumnExample> {
List<String> data = ['Item 1', 'Item 2', 'Item 3', 'Item 4', 'Item 5'];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Dynamic Column Example'),
),
body: SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
children: [
for (String item in data)
ListTile(
title: Text(item),
// Add any additional widgets or functionality here
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
// Add a new item to the list
setState(() {
data.add('New Item');
});
},
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
Explanation of the Code:
- The primary change is replacing the
ListView.builderwith aSingleChildScrollViewcontaining aColumn. - Instead of using
ListView.builderto dynamically create list items, we now use aforloop within theColumn. This loop iterates through thedatalist, creating aListTilefor each item. - The
SingleChildScrollViewallows theColumnto be scrollable, similar to how aListViewfunctions. - The rest of the code remains mostly the same, including the FloatingActionButton for adding new items to the list.
Output:
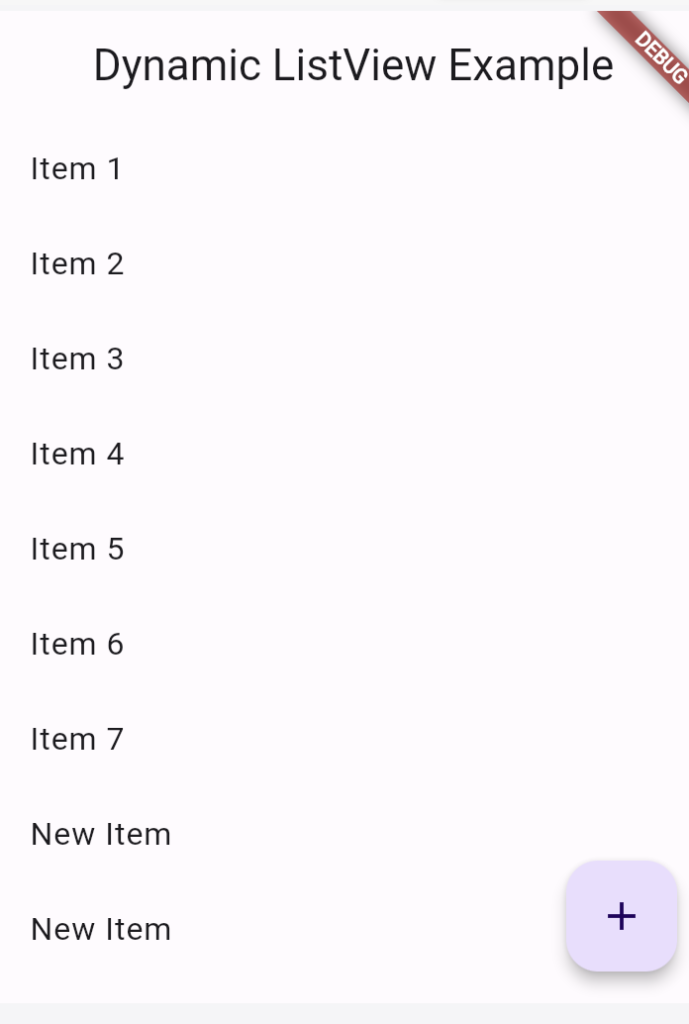
Also Read:
Conclusion
While a Column within a SingleChildScrollView can be suitable for simple layouts, utilizing ListView is often a better choice when dealing with dynamic or large datasets.
The provided code example showcases the efficiency and simplicity of implementing a dynamic ListView in Flutter.
Experiment with this example in your Flutter projects to harness the benefits of ListView for improved performance and a more responsive user interface.
